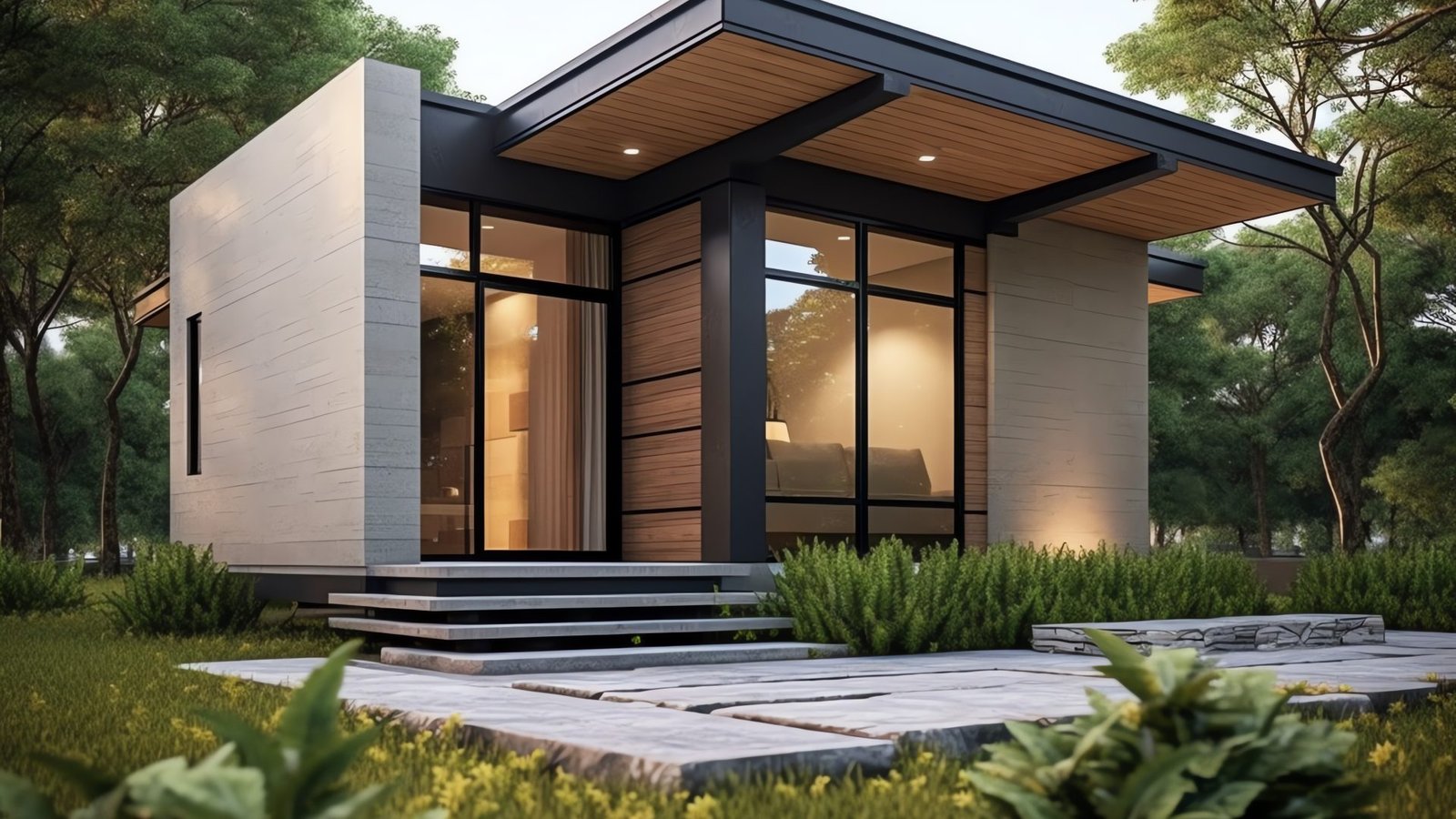
Tiny houses have gained popularity in recent years as a sustainable and minimalist housing option that offers a simpler way of living. These compact dwellings typically range from 100 to 400 square feet in size, emphasizing efficient use of space and resources. Despite their small footprint, tiny houses are designed to maximize functionality and comfort, often incorporating innovative storage solutions, multi-purpose furniture, and clever design elements. Many tiny house enthusiasts are drawn to the idea of downsizing and reducing their environmental impact, as these homes require fewer materials to build and consume less energy for heating and cooling. Additionally, tiny houses can be mobile or stationary, providing flexibility for those seeking a more nomadic lifestyle or looking to reduce housing costs. Overall, tiny houses offer a unique and sustainable housing alternative that promotes simplicity, mindfulness, and a closer connection to the environment.
Method
Tiny houses are typically built using a variety of construction techniques, materials, and design principles to maximize space efficiency and functionality. Some common methods include traditional stick-built construction, modular construction, and prefabrication. Stick-built construction involves building the tiny house on-site using traditional building materials such as wood framing, insulation, and siding. Modular construction involves constructing individual modules or sections of the tiny house in a factory setting and then assembling them on-site. Prefabrication involves building components of the tiny house off-site and then assembling them on-site, reducing construction time and costs. Additionally, sustainable building practices such as using eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and passive design strategies are often incorporated into the construction of tiny houses to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability.
SEE PROJECTS
